Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Join our community and stay updated.
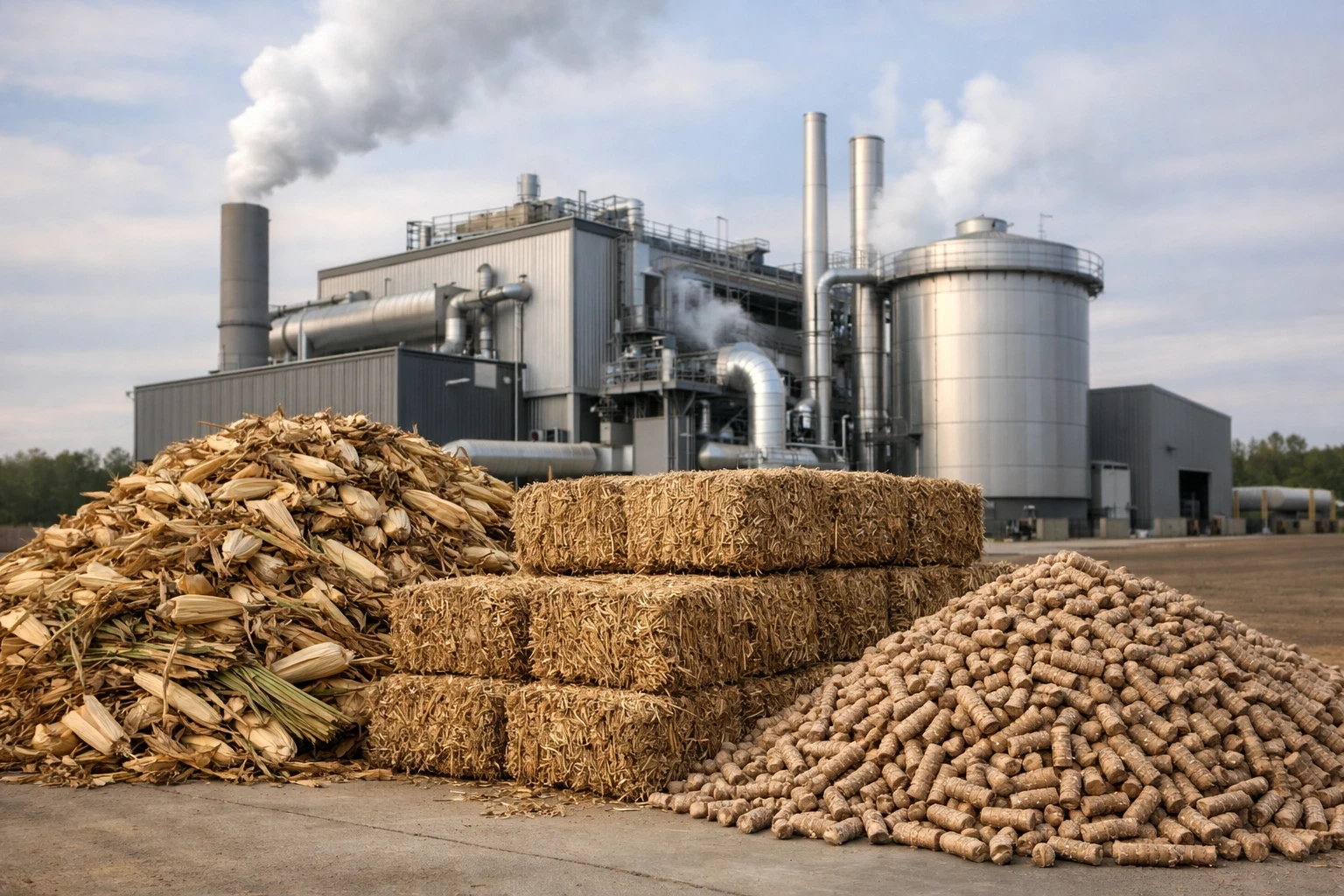

As the demand for cleaner and more reliable energy grows, many industries and communities are turning toward renewable sources. One such source is biomass. While the term is often mentioned in discussions around energy and biofuel, it is not always clearly explained.
This article talks about what biomass is, how it is used, and what biomass energy is used for in practical, real-world terms.
Biomass refers to organic material that comes from plants and animals. These materials store energy from the sun, which plants absorb during photosynthesis. When biomass is used as fuel, this stored energy can be released and converted into usable power.
Because biomass comes from organic matter that can be replenished over time, it is commonly used as a renewable energy source.
Biomass is used mainly as a source of energy. Depending on how it is processed, it can provide heat, electricity, or fuel for different applications. This flexibility allows biomass to be used across a wide range of sectors, from small-scale heating systems to large industrial operations.
One of the most common uses of biomass is for generating heat. Biomass fuels such as wood pellets, briquettes, or agricultural waste are burned to produce heat. This heat is often used: In manufacturing unitsIn food processing plantsFor space heating in commercial buildingsIn many industries, biomass is used in boilers to generate steam required for daily operations.
Biomass is also used to produce electricity. In this process, biomass fuel is burned to heat water, producing steam that drives turbines connected to generators. This approach is commonly used in biomass power plants and in facilities that generate both heat and electricity.
Industries with high energy demands often use biomass as a steady fuel source. Sectors such as textiles, chemicals, paper, and packaging rely on biomass to meet thermal energy needs and support continuous production processes. Suppliers like Edhas Biofuel support these industries by providing biomass solutions suited to industrial-scale energy use.
Biomass energy is created by converting organic material into usable power. Several established methods are used for this purpose, each suited to different types of biomass.
Combustion is the most direct method of using biomass. The biomass fuel is burned to release heat energy, which can be used directly or converted into electricity. Combustion systems are commonly used in boilers and power plants.
In gasification, biomass is heated in a low-oxygen environment. This produces a gas mixture that can be burned to generate heat or electricity. This method is used in systems where controlled energy output is required.
Some types of biomass, particularly wet organic waste, are broken down by microorganisms in the absence of oxygen. This process produces biogas, which can be used as fuel for heating or power generation. Together, these methods explain how biomass energy is used across different applications.
Biomass energy is used wherever a consistent source of heat or power is needed.
Common applications include:
In many cases, biomass energy is integrated into existing energy systems to support uninterrupted operations.
Although biomass energy is often associated with large industrial facilities, it also supports everyday activities. Electricity generated from biomass-powered plants and products manufactured using biomass-generated heat are part of daily life, even if they are not always visible to end users.
Biomass is organic material that holds stored energy from natural processes. When used appropriately, it provides heat, electricity, and fuel across residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Understanding what biomass is used for, how biomass is used, and what biomass energy is used for helps clarify its role in modern energy systems. As interest in renewable energy continues to grow, biomass remains a practical and widely adopted option for meeting energy needs while making effective use of organic resources. Edhas Biofuel contributes to this ecosystem by supporting the responsible supply and use of biomass for energy generation.
Biomass is organic material from plants and animals that can be used as a source of energy.
Biomass is used to produce heat, electricity, and fuel for industrial, commercial, and power generation needs.
Biomass is converted into energy through processes such as combustion, gasification, and anaerobic digestion.
Biomass energy is used for electricity generation, industrial heating, steam production, and fuel applications.
Common biomass materials include agricultural residues, wood waste, organic industrial waste, and energy crops.

Get the latest updates on renewable energy, sustainability trends, and our initiatives delivered straight to your inbox.